W3cubDocs
/CodeceptJSTypeScript
CodeceptJS supports type declaration (opens new window) for TypeScript (opens new window). It means that you can write your tests in TS. Also, all of your custom steps can be written in TS
Why TypeScript?
With the TypeScript writing CodeceptJS tests becomes much easier. If you configure TS properly in your project as well as your IDE, you will get the following features:
- Autocomplete (with InteliSence) (opens new window) - a tool that streamlines your work by suggesting when you typing what function or property which exists in a class, what arguments can be passed to that method, what it returns, etc. Example:
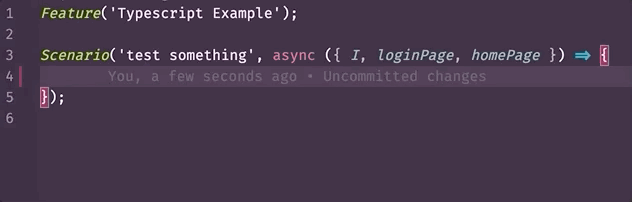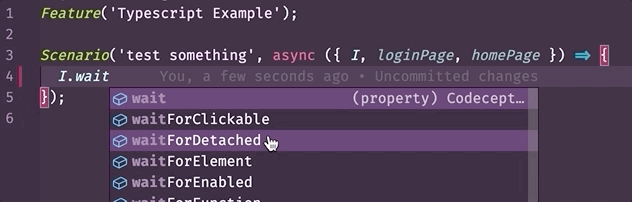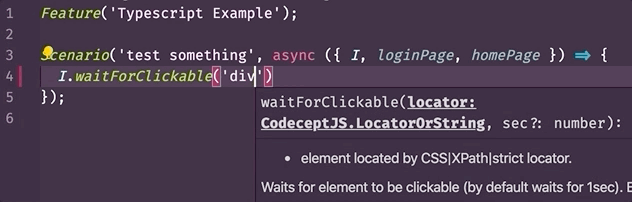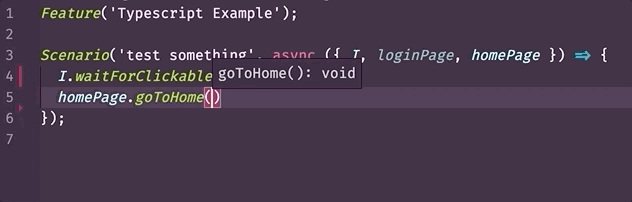
- To show additional information for a step in a test. Example:
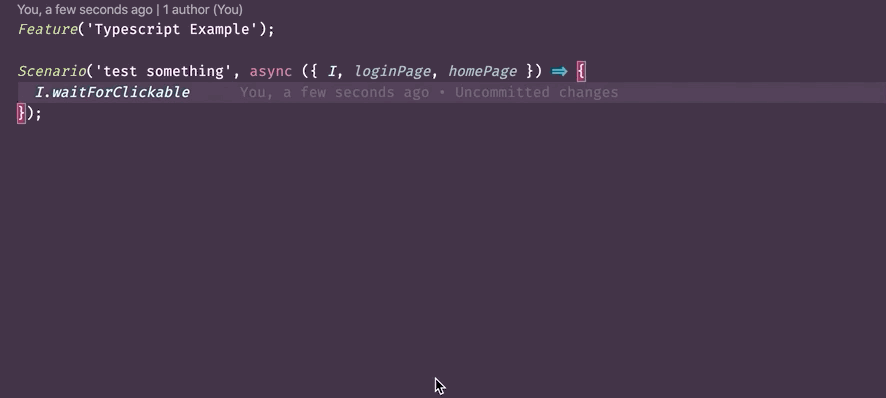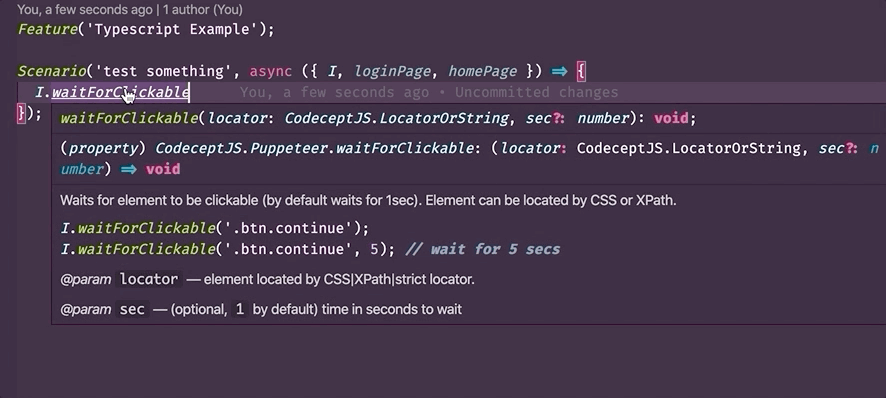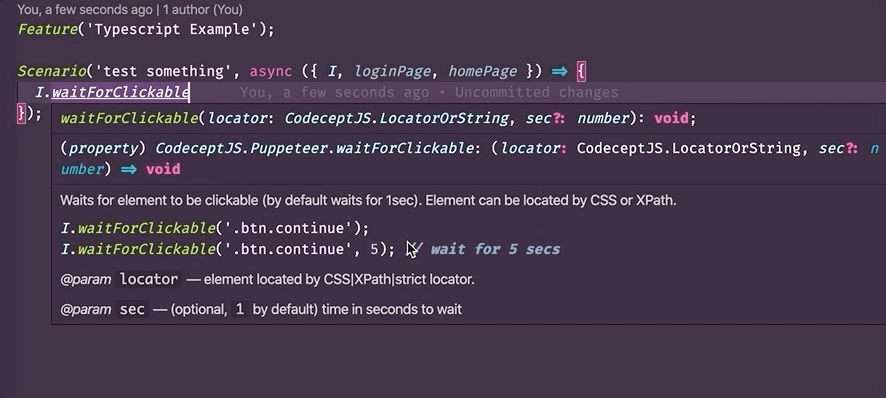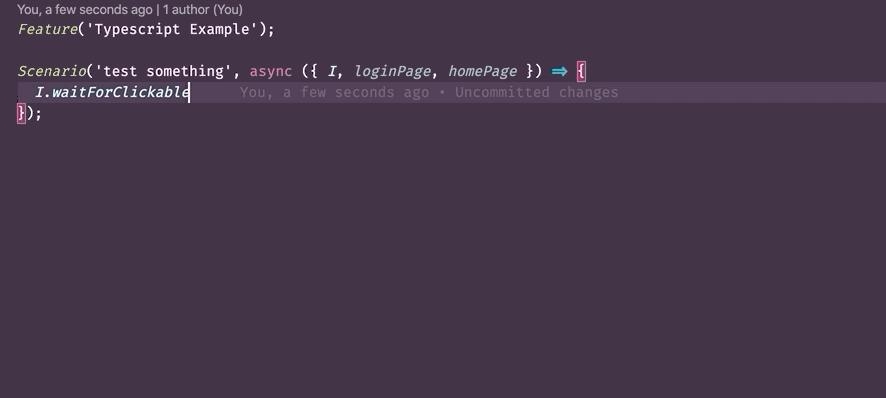
- Checks types - thanks to TypeScript support in CodeceptJS now allow to tests your tests. TypeScript can prevent some errors:
- invalid type of variables passed to function;
- calls no-exist method from PageObject or
Iobject; - incorrectly used CodeceptJS features;
Getting Started
TypeScript Boilerplate
To get started faster we prepared typescript boilerplate project (opens new window) which can be used instead of configuring TypeScript on your own. Clone this repository into an empty folder and you are done.
Otherwise, follow next steps to introduce TypeScript into the project.
Install TypeScipt
For writing tests in TypeScript you'll need to install typescript and ts-node into your project.
npm install typescript ts-node
Configure codecept.conf.js
To configure TypeScript in your project, you need to add ts-node/register (opens new window) on first line in your config. Like in the following config file:
require('ts-node/register')
exports.config = {
tests: './*_test.ts',
output: './output',
helpers: {
Puppeteer: {
url: 'http://example.com',
},
},
name: 'project name',
}
Configure tsconfig.json
We recommended the following configuration in a tsconfig.json (opens new window):
{
"ts-node": {
"files": true
},
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es2018",
"lib": ["es2018", "DOM"],
"esModuleInterop": true,
"module": "commonjs",
"strictNullChecks": true,
"types": ["codeceptjs"],
},
}
You can find an example project with TypeScript and CodeceptJS on our project typescript-boilerplate (opens new window).
Set Up steps.d.ts
Configuring the tsconfig.json and codecept.conf.js is not enough, you will need to configure the steps.d.ts file for custom steps. Just simply do this by running this command::
npx codeceptjs def
As a result, a file will be created on your root folder with following content:
/// <reference types='codeceptjs' />
declare namespace CodeceptJS {
interface SupportObject { I: I }
interface Methods extends Puppeteer {}
interface I extends WithTranslation<Methods> {}
namespace Translation {
interface Actions {}
}
}
Types for custom helper or page object
If you want to get types for your custom helper (opens new window), you can add their automatically with CodeceptJS command npx codeceptjs def.
For example, if you add the new step printMessage for your custom helper like this:
// customHelper.ts
class CustomHelper extends Helper {
printMessage(msg: string) {
console.log(msg)
}
}
export = CustomHelper
Then you need to add this helper to your codecept.conf.js like in this docs (opens new window). And then run the command npx codeceptjs def.
As result our steps.d.ts file will be updated like this:
/// <reference types='codeceptjs' />
type CustomHelper = import('./CustomHelper');
declare namespace CodeceptJS {
interface SupportObject { I: I }
interface Methods extends Puppeteer, CustomHelper {}
interface I extends WithTranslation<Methods> {}
namespace Translation {
interface Actions {}
}
}
And now you can use autocomplete on your test.
Generation types for PageObject looks like for a custom helper, but steps.d.ts will look like:
/// <reference types='codeceptjs' />
type loginPage = typeof import('./loginPage');
type homePage = typeof import('./homePage');
type CustomHelper = import('./CustomHelper');
declare namespace CodeceptJS {
interface SupportObject { I: I, loginPage: loginPage, homePage: homePage }
interface Methods extends Puppeteer, CustomHelper {}
interface I extends WithTranslation<Methods> {}
namespace Translation {
interface Actions {}
}
}
© 2015 DavertMik <[email protected]> (http://codegyre.com)
Licensed under the MIT License.
https://codecept.io/typescript/