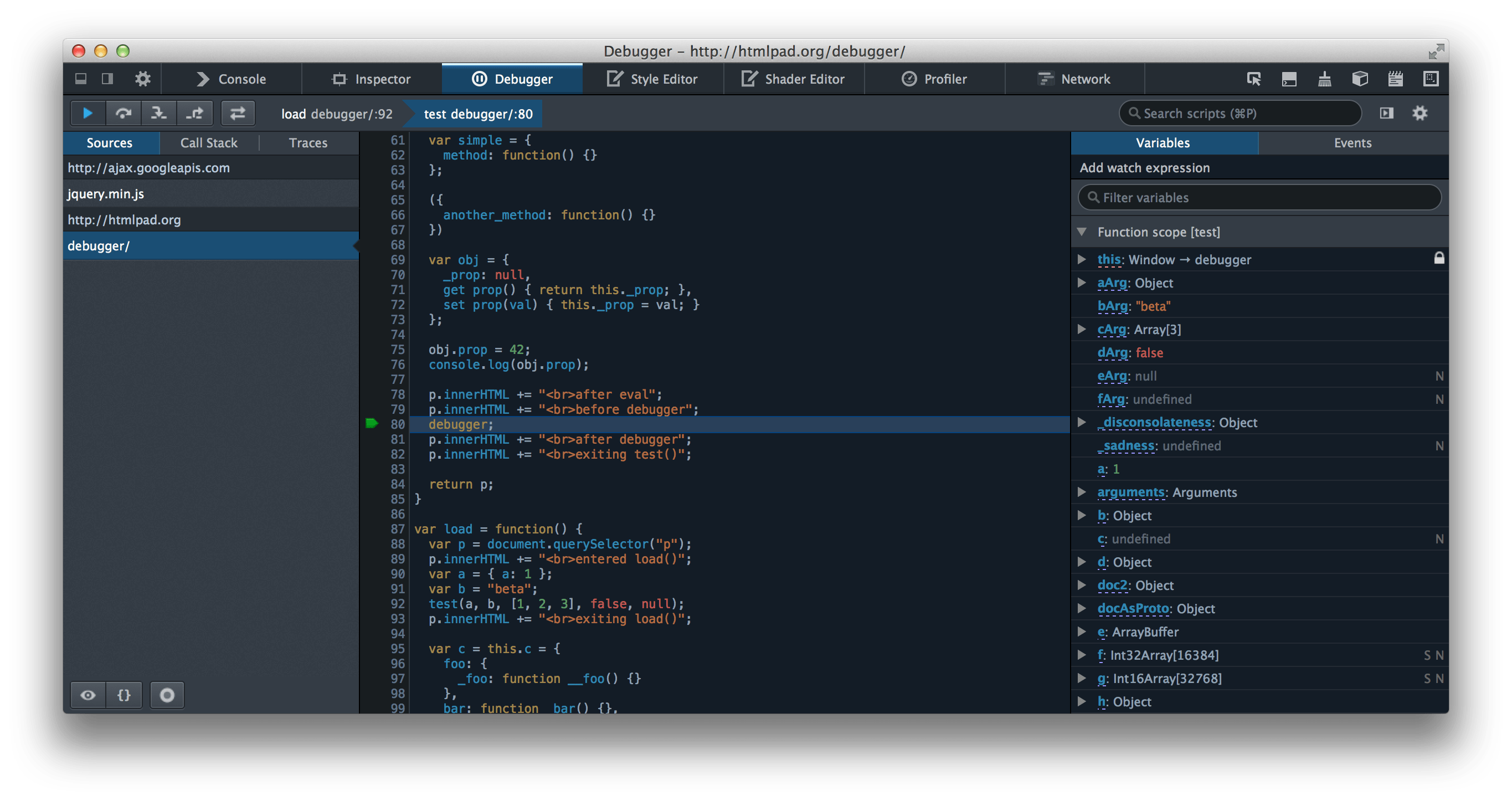
The debugger statement invokes any available debugging functionality, such as setting a breakpoint. If no debugging functionality is available, this statement has no effect.
W3cubDocs
/JavaScriptdebugger
Syntax
js
debugger;
Examples
Using the debugger statement
The following example shows code where a debugger statement has been inserted, to invoke a debugger (if one exists) when the function is called.
js
function potentiallyBuggyCode() { debugger; // do potentially buggy stuff to examine, step through, etc. }
When the debugger is invoked, execution is paused at the debugger statement. It is like a breakpoint in the script source.
Specifications
Browser compatibility
| Desktop | Mobile | Server | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chrome | Edge | Firefox | Opera | Safari | Chrome Android | Firefox for Android | Opera Android | Safari on IOS | Samsung Internet | WebView Android | Deno | Node.js | ||
debugger |
5 | 12 | 1 | 10 | 5 | 18 | 4 | 10.1 | 4.2 | 1.0 | 4.4 | 1.0 | 0.10.0 | |
See also
- The Firefox JavaScript Debugger¶ in the Firefox source docs
© 2005–2023 MDN contributors.
Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License v2.5 or later.
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Statements/debugger