W3cubDocs
/ReactLifting State Up
Often, several components need to reflect the same changing data. We recommend lifting the shared state up to their closest common ancestor. Let’s see how this works in action.
In this section, we will create a temperature calculator that calculates whether the water would boil at a given temperature.
We will start with a component called BoilingVerdict. It accepts the celsius temperature as a prop, and prints whether it is enough to boil the water:
function BoilingVerdict(props) {
if (props.celsius >= 100) {
return <p>The water would boil.</p>;
}
return <p>The water would not boil.</p>;
} Next, we will create a component called Calculator. It renders an <input> that lets you enter the temperature, and keeps its value in this.state.temperature.
Additionally, it renders the BoilingVerdict for the current input value.
class Calculator extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleChange = this.handleChange.bind(this);
this.state = {temperature: ''};
}
handleChange(e) {
this.setState({temperature: e.target.value});
}
render() {
const temperature = this.state.temperature;
return (
<fieldset>
<legend>Enter temperature in Celsius:</legend>
<input value={temperature} onChange={this.handleChange} />
<BoilingVerdict celsius={parseFloat(temperature)} />
</fieldset>
);
}
} Adding a Second Input
Our new requirement is that, in addition to a Celsius input, we provide a Fahrenheit input, and they are kept in sync.
We can start by extracting a TemperatureInput component from Calculator. We will add a new scale prop to it that can either be "c" or "f":
const scaleNames = {
c: 'Celsius',
f: 'Fahrenheit'
};
class TemperatureInput extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleChange = this.handleChange.bind(this);
this.state = {temperature: ''};
}
handleChange(e) {
this.setState({temperature: e.target.value});
}
render() {
const temperature = this.state.temperature;
const scale = this.props.scale;
return (
<fieldset>
<legend>Enter temperature in {scaleNames[scale]}:</legend>
<input value={temperature}
onChange={this.handleChange} />
</fieldset>
);
}
} We can now change the Calculator to render two separate temperature inputs:
class Calculator extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<TemperatureInput scale="c" />
<TemperatureInput scale="f" />
</div>
);
}
} We have two inputs now, but when you enter the temperature in one of them, the other doesn’t update. This contradicts our requirement: we want to keep them in sync.
We also can’t display the BoilingVerdict from Calculator. The Calculator doesn’t know the current temperature because it is hidden inside the TemperatureInput.
Writing Conversion Functions
First, we will write two functions to convert from Celsius to Fahrenheit and back:
function toCelsius(fahrenheit) {
return (fahrenheit - 32) * 5 / 9;
}
function toFahrenheit(celsius) {
return (celsius * 9 / 5) + 32;
} These two functions convert numbers. We will write another function that takes a string temperature and a converter function as arguments and returns a string. We will use it to calculate the value of one input based on the other input.
It returns an empty string on an invalid temperature, and it keeps the output rounded to the third decimal place:
function tryConvert(temperature, convert) {
const input = parseFloat(temperature);
if (Number.isNaN(input)) {
return '';
}
const output = convert(input);
const rounded = Math.round(output * 1000) / 1000;
return rounded.toString();
} For example, tryConvert('abc', toCelsius) returns an empty string, and tryConvert('10.22', toFahrenheit) returns '50.396'.
Lifting State Up
Currently, both TemperatureInput components independently keep their values in the local state:
class TemperatureInput extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleChange = this.handleChange.bind(this);
this.state = {temperature: ''};
}
handleChange(e) {
this.setState({temperature: e.target.value});
}
render() {
const temperature = this.state.temperature;
// ... However, we want these two inputs to be in sync with each other. When we update the Celsius input, the Fahrenheit input should reflect the converted temperature, and vice versa.
In React, sharing state is accomplished by moving it up to the closest common ancestor of the components that need it. This is called “lifting state up”. We will remove the local state from the TemperatureInput and move it into the Calculator instead.
If the Calculator owns the shared state, it becomes the “source of truth” for the current temperature in both inputs. It can instruct them both to have values that are consistent with each other. Since the props of both TemperatureInput components are coming from the same parent Calculator component, the two inputs will always be in sync.
Let’s see how this works step by step.
First, we will replace this.state.temperature with this.props.temperature in the TemperatureInput component. For now, let’s pretend this.props.temperature already exists, although we will need to pass it from the Calculator in the future:
render() {
// Before: const temperature = this.state.temperature;
const temperature = this.props.temperature;
// ... We know that props are read-only. When the temperature was in the local state, the TemperatureInput could just call this.setState() to change it. However, now that the temperature is coming from the parent as a prop, the TemperatureInput has no control over it.
In React, this is usually solved by making a component “controlled”. Just like the DOM <input> accepts both a value and an onChange prop, so can the custom TemperatureInput accept both temperature and onTemperatureChange props from its parent Calculator.
Now, when the TemperatureInput wants to update its temperature, it calls this.props.onTemperatureChange:
handleChange(e) {
// Before: this.setState({temperature: e.target.value});
this.props.onTemperatureChange(e.target.value);
// ... Note:
There is no special meaning to either
temperatureoronTemperatureChangeprop names in custom components. We could have called them anything else, like name themvalueandonChangewhich is a common convention.
The onTemperatureChange prop will be provided together with the temperature prop by the parent Calculator component. It will handle the change by modifying its own local state, thus re-rendering both inputs with the new values. We will look at the new Calculator implementation very soon.
Before diving into the changes in the Calculator, let’s recap our changes to the TemperatureInput component. We have removed the local state from it, and instead of reading this.state.temperature, we now read this.props.temperature. Instead of calling this.setState() when we want to make a change, we now call this.props.onTemperatureChange(), which will be provided by the Calculator:
class TemperatureInput extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleChange = this.handleChange.bind(this);
}
handleChange(e) {
this.props.onTemperatureChange(e.target.value);
}
render() {
const temperature = this.props.temperature;
const scale = this.props.scale;
return (
<fieldset>
<legend>Enter temperature in {scaleNames[scale]}:</legend>
<input value={temperature}
onChange={this.handleChange} />
</fieldset>
);
}
} Now let’s turn to the Calculator component.
We will store the current input’s temperature and scale in its local state. This is the state we “lifted up” from the inputs, and it will serve as the “source of truth” for both of them. It is the minimal representation of all the data we need to know in order to render both inputs.
For example, if we enter 37 into the Celsius input, the state of the Calculator component will be:
{
temperature: '37',
scale: 'c'
} If we later edit the Fahrenheit field to be 212, the state of the Calculator will be:
{
temperature: '212',
scale: 'f'
} We could have stored the value of both inputs but it turns out to be unnecessary. It is enough to store the value of the most recently changed input, and the scale that it represents. We can then infer the value of the other input based on the current temperature and scale alone.
The inputs stay in sync because their values are computed from the same state:
class Calculator extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleCelsiusChange = this.handleCelsiusChange.bind(this);
this.handleFahrenheitChange = this.handleFahrenheitChange.bind(this);
this.state = {temperature: '', scale: 'c'};
}
handleCelsiusChange(temperature) {
this.setState({scale: 'c', temperature});
}
handleFahrenheitChange(temperature) {
this.setState({scale: 'f', temperature});
}
render() {
const scale = this.state.scale;
const temperature = this.state.temperature;
const celsius = scale === 'f' ? tryConvert(temperature, toCelsius) : temperature;
const fahrenheit = scale === 'c' ? tryConvert(temperature, toFahrenheit) : temperature;
return (
<div>
<TemperatureInput
scale="c"
temperature={celsius} onTemperatureChange={this.handleCelsiusChange} /> <TemperatureInput
scale="f"
temperature={fahrenheit} onTemperatureChange={this.handleFahrenheitChange} /> <BoilingVerdict
celsius={parseFloat(celsius)} /> </div>
);
}
} Now, no matter which input you edit, this.state.temperature and this.state.scale in the Calculator get updated. One of the inputs gets the value as is, so any user input is preserved, and the other input value is always recalculated based on it.
Let’s recap what happens when you edit an input:
- React calls the function specified as
onChangeon the DOM<input>. In our case, this is thehandleChangemethod in theTemperatureInputcomponent. - The
handleChangemethod in theTemperatureInputcomponent callsthis.props.onTemperatureChange()with the new desired value. Its props, includingonTemperatureChange, were provided by its parent component, theCalculator. - When it previously rendered, the
Calculatorhad specified thatonTemperatureChangeof the CelsiusTemperatureInputis theCalculator’shandleCelsiusChangemethod, andonTemperatureChangeof the FahrenheitTemperatureInputis theCalculator’shandleFahrenheitChangemethod. So either of these twoCalculatormethods gets called depending on which input we edited. - Inside these methods, the
Calculatorcomponent asks React to re-render itself by callingthis.setState()with the new input value and the current scale of the input we just edited. - React calls the
Calculatorcomponent’srendermethod to learn what the UI should look like. The values of both inputs are recomputed based on the current temperature and the active scale. The temperature conversion is performed here. - React calls the
rendermethods of the individualTemperatureInputcomponents with their new props specified by theCalculator. It learns what their UI should look like. - React calls the
rendermethod of theBoilingVerdictcomponent, passing the temperature in Celsius as its props. - React DOM updates the DOM with the boiling verdict and to match the desired input values. The input we just edited receives its current value, and the other input is updated to the temperature after conversion.
Every update goes through the same steps so the inputs stay in sync.
Lessons Learned
There should be a single “source of truth” for any data that changes in a React application. Usually, the state is first added to the component that needs it for rendering. Then, if other components also need it, you can lift it up to their closest common ancestor. Instead of trying to sync the state between different components, you should rely on the top-down data flow.
Lifting state involves writing more “boilerplate” code than two-way binding approaches, but as a benefit, it takes less work to find and isolate bugs. Since any state “lives” in some component and that component alone can change it, the surface area for bugs is greatly reduced. Additionally, you can implement any custom logic to reject or transform user input.
If something can be derived from either props or state, it probably shouldn’t be in the state. For example, instead of storing both celsiusValue and fahrenheitValue, we store just the last edited temperature and its scale. The value of the other input can always be calculated from them in the render() method. This lets us clear or apply rounding to the other field without losing any precision in the user input.
When you see something wrong in the UI, you can use React Developer Tools to inspect the props and move up the tree until you find the component responsible for updating the state. This lets you trace the bugs to their source:
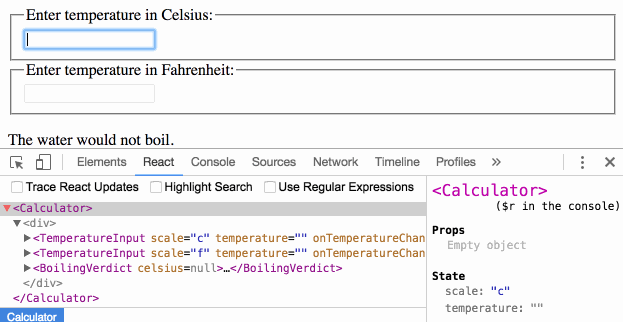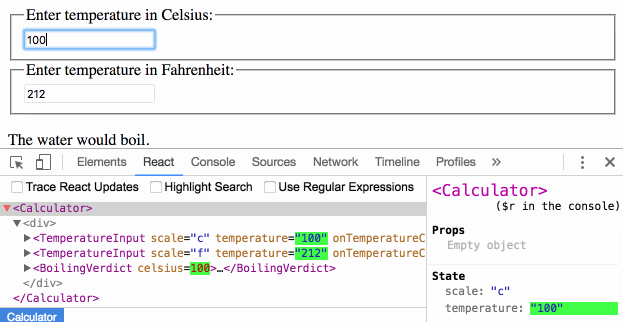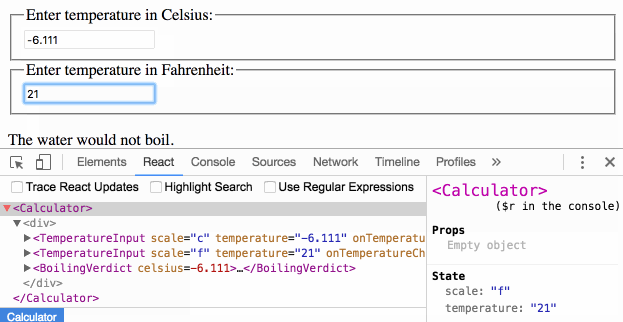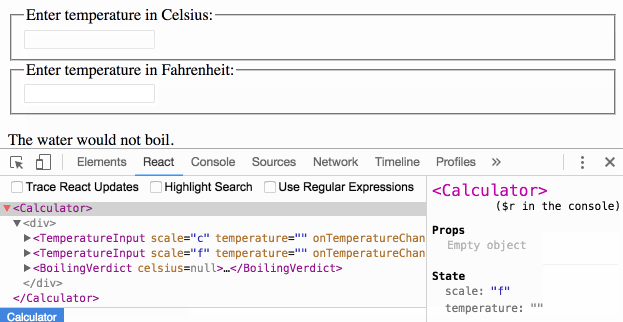 Is this page useful?
Is this page useful?
© 2013–present Facebook Inc.
Licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Public License.
https://reactjs.org/docs/lifting-state-up.html